5 Best Diets To Lose Weight Fast: Guide To Healthy Eating for Rapid Weight Loss
Some links on this page are affiliate links (including Amazon Associate links) which means that, if you choose to make a purchase, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. We greatly appreciate your support!
Choosing the right diet can be the difference between temporary weight loss and lasting transformation. As obesity rates continue to rise, understanding evidence-based dietary approaches has never been more critical. This comprehensive guide breaks down the best diets to lose weight, their unique benefits, and how to select the perfect nutrition plan for your individual weight loss goals.
Weight Loss Plans: Key Considerations For The Best Diets To Lose Weight
Metabolism and Individual Body Composition Factors
Everyone’s body burns energy a little differently. That’s mostly because of metabolism—how your body turns food into energy. Things like age, muscle mass, activity level, and genetics all play a big role. Someone with more muscle might burn more calories at rest, while someone else might have a naturally slower metabolism.
This is why two people can eat the exact same foods and see completely different results. Understanding your body’s unique needs can help you pick a diet that actually works for you and doesn’t leave you feeling frustrated or stuck.
Importance of Sustainable Nutrition Plans
It’s easy to get caught up in a diet that promises fast results, but if it’s too strict or hard to follow, chances are you’ll give it up pretty quickly. A sustainable nutrition plan is something you can stick with for the long haul—not just a few weeks.
That means enjoying real food, feeling satisfied, and building healthy habits that fit into your life. Look for diets that include a good balance of whole foods like fruits, veggies, lean proteins, and whole grains rather than cutting out entire food groups or setting unrealistic rules.
Red Flags in Fad Diets
Some diets make big promises with little science to back them up. If a plan cuts out entire food groups, promotes miracle weight loss pills, or guarantees you’ll lose a ton of weight fast, it’s probably a fad—and it could even be harmful.
Be cautious of diets that don’t explain how they support your health, focus only on calories or numbers on the scale, or leave you feeling tired and hungry all the time. Quick fixes usually don’t last, and they can mess with your metabolism and mindset in the long run.
Role of Personalized Nutrition
Your weight loss journey should be based on your body, goals, and lifestyle—not someone else’s. That’s where personalized nutrition comes in. This means creating an eating plan that works with your tastes, schedule, health needs, and personal preferences.
Whether you’re a vegetarian, have food allergies, or are just super busy, the right approach will be tailored to what works for you. Personalized diets are not only easier to follow—they’re also more likely to give you lasting results.
Medical Considerations Before Starting Any Diet
Before you change your diet in a big way, it’s smart to talk to your doctor, especially if you have health conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, or thyroid issues. Some diets can interact with medications or affect your energy levels and blood sugar.
A healthcare provider or registered dietitian can help you choose the best diet to lose weight that’s safe for you and supports both weight loss and overall health. Getting professional guidance can also keep you from falling into unhealthy or unsafe dieting habits.
Summary
When it comes to losing weight, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. What works for your neighbor or your favorite fitness influencer might not work for you—and that’s okay! Before starting any diet, it’s important to understand how your body works and what to look for in a healthy, long-lasting eating plan. Let’s break down the key things you need to know when considering the best diet to lose weight for you.
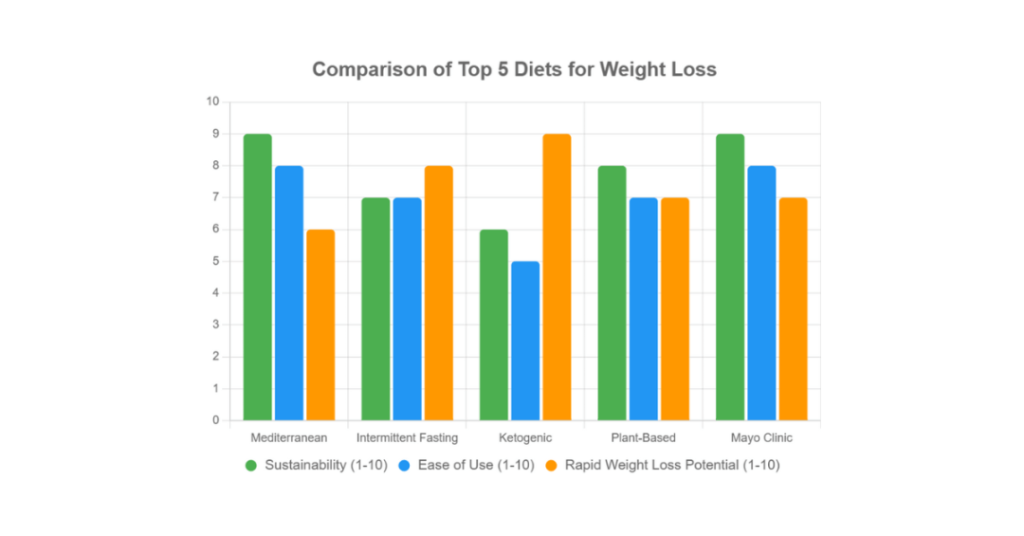
1. Mediterranean Diet: Heart Healthy Eating For Weight Loss
Scientific Evidence of Weight Loss Effectiveness
Multiple studies show that the Mediterranean diet is one of the best diets to lose weight and helps with healthy weight management. One large review published in 2020 in the journal Nutrients found that people who followed this diet lost more weight than those on low-fat plans. Scientists believe this is because the Mediterranean diet is satisfying and rich in fiber and healthy fats, which help control hunger and prevent overeating.
Even better? This way of eating helps keep the weight off for the long haul. Since it doesn’t involve extreme restrictions, many people find it easier to stick with, making it great not just for losing weight, but for keeping it off, too.
Key Food Components
The Mediterranean diet doesn’t focus on counting calories. Instead, it encourages whole, natural foods that fuel your body in a healthy way. Some key foods include:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables (especially leafy greens and tomatoes)
- Whole grains like brown rice, oats, and barley
- Healthy fats such as extra virgin olive oil and nuts
- Lean proteins, mainly fish and seafood
- Legumes like chickpeas and lentils
- Herbs and spices for flavor (instead of salt)
- Small amounts of dairy and red wine (optional)
Red meats and heavily processed foods are limited. Sweet treats are enjoyed only occasionally.
Sample Meal Planning Strategies
Meal planning with the Mediterranean diet is simple, tasty, and flexible. Here’s a basic guide to help you get started:
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt topped with berries, chia seeds, and a drizzle of honey
- Lunch: Quinoa salad with cucumbers, tomatoes, olives, feta, and a lemon-olive oil dressing
- Snack: A handful of almonds or fresh-cut veggies with hummus
- Dinner: Grilled salmon with roasted vegetables and a side of whole-grain couscous
- Dessert (optional): A small piece of dark chocolate or a few fresh figs
Cooking with olive oil and adding herbs like oregano or basil will not only boost flavor but also add extra antioxidants to support your health goals.
Cardiovascular Health Benefits
One of the biggest reasons doctors love the Mediterranean diet is its power to protect your heart. Research links this eating style to lower levels of “bad” LDL cholesterol and reduced risk of heart disease and stroke. In fact, the American Heart Association recommends this diet as a top heart-health option.
The healthy fats from olive oil, nuts, and seafood help support better blood pressure and healthy blood vessels. When combined with more fruits, veggies, and fiber, it creates a powerful mix for both your heart and waistline.
Long-Term Sustainability
What makes the Mediterranean diet so popular year after year? It’s easy to stick to.
There are no complicated rules or foods you must completely cut out. That means you can enjoy meals with your family or eat out without too much stress. People who follow this diet often say they feel more satisfied compared to those on highly restrictive plans. Since it’s not about temporary changes, but a lifestyle shift, it’s perfect for long-term weight control and overall wellness.
Summary
The Mediterranean diet has long been known for its health benefits, especially for your heart. But did you know it’s also one of the best diets for losing weight and keeping it off? It’s still a top choice for people who want to shed pounds without strict rules or cutting out entire food groups. It’s based on the traditional eating habits of countries like Greece, Italy, and Spain and focuses on fresh, whole foods that are good for your body and easy to enjoy.
2. Intermittent Fasting: Metabolic Reset Strategy To Help You Lose Weight Fast
Different Intermittent Fasting Methods
There are several common IF methods, so you can pick one that fits your lifestyle:
- 16:8 Method: Fast for 16 hours and eat during an 8-hour window (like 12 PM to 8 PM).
- 5:2 Diet: Eat normally five days a week and cut calories to about 500–600 on two non-consecutive days.
- Eat-Stop-Eat: Fast for a full 24 hours once or twice a week.
- Alternate-Day Fasting: Every other day, either fast completely or eat a very small number of calories.
- OMAD (One Meal a Day): Eat only once every 24 hours—usually a large, balanced meal.
Many people start with the 16:8 method because it’s easy to adjust to daily life. Skipping breakfast and having your first meal at noon works well for busy schedules.
Short fasting periods help reduce your total calorie intake and can make your body better at burning stored fat.
Hormonal Impacts on Weight Loss
When you fast, your hormone levels shift to help with fat burning:
- Insulin goes down, which helps your body reach into fat stores for energy.
- Human Growth Hormone (HGH) goes up, which may support lean muscle and fat loss.
- Norepinephrine, a fat-burning hormone, increases during fasting to help break down body fat.
These hormone changes make it easier for your body to lose fat and maintain energy—even when you’re not eating.
Potential Health Benefits
Besides weight loss, IF could have other perks supported by early research:
- May reduce inflammation, which is linked to many chronic diseases.
- Can improve blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity—good news for people at risk for type 2 diabetes.
- Might support brain health by boosting mental clarity and concentration.
- Studies in animals suggest it could promote longer lifespans, though more human research is needed.
These bonus effects make IF appealing to people who want both a slimmer body and better overall health.
Implementation Guidelines
Getting started with intermittent fasting doesn’t have to be hard.
- Choose a method that matches your daily routine—many start with 16:8.
- During fasting periods, drink water, black coffee, or unsweetened tea to stay hydrated.
- Don’t binge during eating windows—focus on whole foods, protein, healthy fats, and complex carbs.
- Ease into it. Try a 12-hour fast at first (like 7 PM to 7 AM) and build up from there.
- Listen to your body—some hunger is normal at first, but you shouldn’t feel weak or dizzy.
The goal isn’t to starve yourself—it’s to give your body a new rhythm for burning fat more efficiently.
Potential Risks and Considerations
Intermittent fasting isn’t for everyone. Here are a few things to keep in mind:
- IF may not be suitable for people with diabetes, low blood pressure, or those taking certain medications—always check with your doctor first.
- It’s not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- Some people may overeat during eating windows, which defeats the purpose.
- Extended fasting can lead to fatigue, cravings, irritability, or nutrient deficiencies if not done carefully.
- May trigger disordered eating in people with a history of eating disorders.
Pay attention to how your body reacts. If you’re always tired, overly hungry, or obsessed with food, this method might not work for your lifestyle.
Summary
Intermittent fasting (IF) isn’t really a “diet” in the usual sense—it’s more about when you eat rather than what you eat. It’s become super popular for weight loss because it gives your body a chance to burn stored fat, and many people find that it’s easier to follow than strict calorie-counting.
3. Ketogenic Diet: Low-Carb Diet For Weight Loss
Mechanism of Ketosis
The ketogenic (or “keto”) diet is one of the best diets to lose weight because it changes the way your body uses energy. Normally, your body burns carbs (like bread, pasta, and sugar) for fuel. But when you cut way back on carbs, your body runs out of its usual fuel and starts burning fat instead. This fat-burning state is called “ketosis.” In ketosis, your liver turns fat into tiny fuel molecules called ketones, which your body and brain can use for energy.
When you’re in ketosis, your body becomes a fat-burning machine — and that’s why many people lose weight quickly on keto. It also helps reduce hunger for some people, which makes it easier to eat fewer calories without feeling deprived.
Macronutrient Breakdown
The keto diet is all about changing your daily intake of fats, proteins, and carbs — also known as macronutrients. Here’s a basic breakdown of where your calories come from on a standard keto plan:
- 70–75% fats (like avocado, butter, olive oil, fatty fish)
- 20–25% protein (like eggs, chicken, beef, tofu)
- 5–10% carbohydrates (mostly from leafy greens, nuts, and low-carb vegetables)
That means you’re eating very few carbs—usually around 20 to 50 grams per day. That’s less than one bagel or a small bowl of rice! The goal is to stay low enough in carbs that your body stays in ketosis.
Rapid Initial Weight Loss Potential
One reason keto is so popular for weight loss is that it can lead to fast results — especially in the beginning. In the first one to two weeks, many people drop several pounds. Most of this early weight loss is water weight. That’s because cutting carbs lowers your body’s insulin levels, which makes your body release stored water.
After that, you may continue to lose fat if you stick with the plan. Some people also feel less hungry on keto, which makes it easier to eat less without thinking about it too much. Quick results can be motivating, especially if you’ve struggled with slower weight loss on other diets.
Nutritional Challenges
The keto diet can be very effective, but it’s not always easy. One big challenge? It can be hard to get all the nutrients your body needs when you’re cutting out many fruits, grains, and starchy veggies. You may not get enough fiber either, which can affect digestion.
Another issue is what’s known as the “keto flu.” This often happens in the first few days and may include headaches, fatigue, dizziness, and brain fog. It’s your body adjusting to using fat for fuel instead of carbs.
You also have to be careful about eating too much protein. On keto, eating too much protein can push your body out of ketosis because it might turn some of that protein into sugar. Learning to balance your food intake is key.
Best Practices for Safe Implementation
If you’re thinking about trying keto, it’s best to ease into it and plan your meals ahead of time. Here are some simple tips to help you get started safely:
- Talk to your doctor, especially if you have health issues or take medications.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and help with keto flu symptoms.
- Get enough electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium. These are found in foods like spinach, nuts, and avocados.
- Add fiber-rich, low-carb veggies like broccoli, kale, and cauliflower to support digestion.
- Keep track of your macros (using an app or a food journal) to make sure you stay in ketosis.
Taking it slow and listening to your body helps make the ketogenic diet safer and more effective. Keep in mind that while keto can be powerful for weight loss, it might not be the best fit long-term for everyone.
Summary
The keto diet helps your body burn fat for energy instead of carbs, which can lead to fast weight loss. By eating mostly fats, some protein, and very few carbs, your body enters a state called ketosis. While it can be effective, it’s important to plan carefully and stay balanced to avoid side effects like the “keto flu.”
4. Plant-Based Diet: Whole Food Nutrition Approach To Weight Management
Weight Loss and Metabolic Health Benefits
A plant-based diet can help you shed extra pounds in a way that’s both healthy and lasting. Because plants are naturally low in calories and high in fiber, you’ll likely eat fewer calories without feeling hungry all the time.
Studies show that people who eat mostly plant-based diets often weigh less and have healthier metabolisms. This means your body uses energy more effectively, which makes it easier to keep off the weight you lose. You may also see improvements in blood sugar and cholesterol levels, both of which are good for your heart and long-term weight management.
Protein Sources for Vegetarian/Vegan Diets
One common question about plant-based eating is “Where do I get my protein?” Great news: you can still get plenty of protein without meat or dairy.
Top plant-based protein sources include:
- Lentils and chickpeas
- Black beans, pinto beans, and other legumes
- Tofu, tempeh, and edamame
- Quinoa and whole grains
- Nuts and seeds, like almonds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds
- Plant-based protein powders (look for ones without added sugar)
Mixing a variety of these foods throughout the day can help ensure you’re getting all the essential amino acids your body needs to build muscle and maintain a strong metabolism.
Nutrient Considerations
While a plant-based diet is full of health perks, there are a few key nutrients you’ll want to keep an eye on:
- Vitamin B12: Usually found in animal products, so consider a supplement or fortified foods.
- Iron: Found in foods like lentils and spinach—pair with vitamin C-rich foods (like oranges or bell peppers) to improve absorption.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Try flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, or consider an algae-based supplement.
- Calcium: Found in fortified plant milks, tofu, and leafy greens.
- Zinc and iodine: Check in with a doctor or dietitian if you’re going fully plant-based long term.
Paying attention to these nutrients can help you stay energized, support your metabolism, and avoid any unwanted side effects while losing weight.
Environmental and Ethical Aspects
More and more people are drawn to plant-based diets not only for health reasons but also for environmental and ethical concerns.
Animal farming is one of the biggest sources of greenhouse gases, so eating fewer animal products can significantly lower your carbon footprint. Choosing plant-based also supports the ethical treatment of animals, which is important to many people who care about where their food comes from.
While these might not be the main reasons you start a plant-based diet for weight loss, they’re feel-good bonuses that can help keep you motivated.
Meal Planning Strategies
Planning ahead is key when following a plant-based diet for weight loss. It helps you avoid last-minute unhealthy choices and ensures you’re getting a balance of the nutrients your body needs.
Helpful meal-planning tips:
- Prep in batches: Cook a big pot of beans, grains, or roasted vegetables at the start of the week.
- Keep it colorful: Try to have at least three different colors of veggies at each meal for a range of nutrients.
- Build balanced plates: Aim for a mix of protein (beans, tofu), complex carbs (quinoa, sweet potatoes), and healthy fats (avocado, nuts).
- Use herbs and spices: They boost flavor without adding extra calories or salt.
- Have easy snacks ready: Keep things like fresh fruit, hummus with veggies, or trail mix on hand to avoid processed temptations.
Sticking to a smart plan makes eating plant-based easier, more satisfying, and much better for weight loss success.
Summary
Choosing a plant-based diet can be a great way to lose weight while supporting your overall health. This type of eating focuses on whole, natural foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Unlike processed foods or fad diets, plant-based meals are rich in fiber and nutrients, making you feel full while still helping you cut down on calories.
5. The Mayo Clinic Diet: Doctor-Developed Dietary Plan for Lasting Weight-Loss
Healthy Habits and Steady Weight Loss
One of the best diets to lose weight, the Mayo Clinic Diet uses a two-phase approach. In the “Lose It!” phase, you jumpstart weight loss by breaking five unhealthy habits (like eating while watching TV) and adding five new ones (like eating a healthy breakfast every day). Most people lose 6 to 10 pounds in the first two weeks! The second phase—“Live It!”—helps you continue losing weight at a steady pace and maintain it long term by sticking to smart eating, regular activity, and portion control.
This isn’t about crash dieting—it’s about building a foundation of habits you can actually live with.
Core Food Groups and Smart Choices
The Mayo Clinic Diet encourages you to eat more of the good stuff and less of the not-so-good. The food pyramid used in this plan puts the focus on:
- Fruits and vegetables: These should take up the biggest part of your plate. They’re naturally low in calories and high in fiber, which means you’ll feel full and satisfied.
- Whole grains: Think brown rice, oatmeal, and whole wheat bread- great for energy and digestion.
- Lean protein: Chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes are all encouraged in moderation.
- Healthy fats: Small servings of nuts, seeds, and olive oil can support heart health.
- Sweets: Allowed in limited amounts-this is a realistic diet, not a punishment!
This food guide makes it easy to plan meals that are both delicious and diet-friendly.
Portion Control Without The Hassle
One of the best parts of the Mayo Clinic Diet is its built-in portion control strategy. The plan uses visual cues (like “a serving of meat should be about the size of a deck of cards”) to make it easier to eat the right amount—without obsessing over calories.
Some quick tips:
- Use your hands to estimate serving sizes (your fist = 1 cup).
- Fill half your plate with veggies at each meal.
- Eat slowly and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness signals.
This smart approach helps prevent overeating while still letting you enjoy your favorite foods in moderation.
Science-Backed Results You Can Trust
The Mayo Clinic Diet is built on years of clinical experience and medical research. It’s been shown to help people:
- Lose weight gradually and keep it off.
- Lower blood sugar and improve heart health.
- Reduce the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes.
Because it’s developed by health professionals—not influencers—it ranks high on the list of recommended diets by doctors and nutritionists. It’s not just effective—it’s safe and sensible, too.
Simple Steps To Get Started
What makes the Mayo Clinic Diet stick? It’s practical, flexible, and easy to start:
- Set realistic weight loss goals and track your progress.
- Use the Mayo Clinic’s food tracker or journal to stay accountable.
- Prep meals in advance to avoid impulsive eating.
Find a workout you enjoy—even daily walks count!
You don’t have to be perfect—just consistent. With the Mayo Clinic Diet, small changes lead to big results over time.
Summary
The Mayo Clinic Diet isn’t just another trend—it’s a sustainable weight loss plan created by medical experts. Designed by doctors at the world-renowned Mayo Clinic, this diet helps you shed pounds safely while building healthier habits for life. Instead of focusing on what you can’t eat, it emphasizes positive lifestyle changes that help you take control of your weight and overall health.
Tracking and Maintaining Weight Loss Success
Setting Realistic Weight Loss Goals
Setting goals is a big part of staying motivated. But make sure they’re doable! Aiming to lose 1 to 2 pounds per week is safe and manageable for most people. Trying to lose too much too fast can leave you feeling tired, stressed, and more likely to quit.
Focus on small, short-term goals like “drink more water every day” or “exercise three times a week.” Celebrate each success — they all add up! Over time, these small wins lead to major progress you can be proud of.
Importance of Consistent Monitoring
Keeping track of your weight and habits can help you stay in control. Whether it’s stepping on the scale once a week or logging your meals in an app, monitoring helps you spot patterns — like emotional eating or slowing progress — before they become problems.
You don’t have to track everything forever, but checking in regularly gives you a clearer picture of what’s working and what needs adjusting. Think of it as your personal progress report!
Metabolic Adaptation Strategies
As you lose weight, your body adjusts by slowing down metabolism — this is called metabolic adaptation. It’s natural, but it can make weight loss harder over time. The good news is, there are strategies to handle it.
Include regular strength training to help build muscle (which burns more calories). Make sure you’re eating enough protein and not cutting calories too low. Taking occasional “maintenance breaks” with higher calories can also support your metabolism while giving your body and brain a needed reset.
Psychological Aspects of Diet Success
Weight loss isn’t just physical — it’s mental too! Understanding your motivation, stress levels, and emotional eating habits is just as important as diet and exercise.
Practices like journaling, getting support from friends or a coach, and being kind to yourself during setbacks can make a huge difference. Weight loss is a journey with ups and downs, and the more you take care of your mental health, the easier it is to stay on track.
Preventing Weight Loss Plateaus
Hitting a weight loss plateau is totally normal, but it can be frustrating. After a while, your body gets used to your routine and progress slows.
To bust through a plateau, try switching up your workouts, adjusting your calorie intake (either up or down), or focusing on sleep and stress management — which both affect weight loss more than you might think. Staying flexible and open to change is key when your progress stalls.
Summary
Losing weight is one thing — keeping it off is another. Tracking your progress and keeping your body and mind in the right place is key to long-term success. You can stay on track with effective goal setting, monitoring, and smart strategies that support both your body and mindset.
Conclusion
Selecting the best diet to lose weight is a personal journey that requires understanding your body, lifestyle, and health goals. No single approach works for everyone, but armed with scientific information and personalized strategies, you can find a sustainable path to lasting weight loss. Consult with healthcare professionals, listen to your body, and remember that consistency and patience are key to transformative results!





